building home lab part 1
Table of Content
building home lab part 1¶
The machines I actually use to run my kubernetes cluster is on baremetals, but similar setup can be done using virtual machines. In this page I am going to build a separate kubernetes cluster using virtual machines running on hyper-v.
This page will cover the brief introduction of the nodes, setting up gitops using flux, and preparing sops for secret encryption.
node list¶
See hyper-v setup page on the virtual machines were created. They were installed using debian-12.4.0-amd64-netinst.iso image and preseed files.
Here is the list of nodes. The first one is the control plane.
- vcp.hyperv.blink-1x52.net
- vworker1.hyperv.blink-1x52.net
- vworker2.hyperv.blink-1x52.net
- vworker3.hyperv.blink-1x52.net
vworker4.hyperv.blink-1x52.net- vworker5.hyperv.blink-1x52.net
node setup¶
I used ansible playbook to do the followings:
- copy ssh key
- create ansible user and group
- install sudo and enable password-less sudo for the ansible group
- disable swap
- configure iptables and syctl networking
- install and configure containerd, cni, and runc
- install kubeadm, kubelet, and kubectl
- create kubernetes cluster on control plane
- join other worker nodes
- export kubeconfig file
This part is basically doing what kubernetes official document is explaining to do as prerequisite, and I've also posted a blog post in Japanese here - Kubernetesクラスタ構築 - おうちでGitOpsシリーズ投稿2/6, however, I am planning to add a link to separate page or public repository to share the actual ansible playbooks used.
apply network addon to the cluster¶
And then I manually applied calico installation manifests to make the cluster ready for service.
https://github.com/projectcalico/calico
cd ~/dnld
export KUBECONFIG={exported config file here}
# confirm the latest version on cli
curl -sfL "api.github.com/repos/projectcalico/calico/releases/latest" | grep "tag_name"
# download v3.27.0
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.27.0/manifests/tigera-operator.yaml
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.27.0/manifests/custom-resources.yaml
# modify custom-resources.yaml
# and then apply
kubectl create -f tigera-operator.yaml
kubectl create -f custom-resources.yaml
# watch and wait for everything to be ready
watch kubectl get pods -n calico-system -o wide
# allow control plane to work
kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane-
Here is my calico custom-resources.yaml file. I just changed cidr.
# This section includes base Calico installation configuration.
# For more information, see: https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/reference/installation/api#operator.tigera.io/v1.Installation
apiVersion: operator.tigera.io/v1
kind: Installation
metadata:
name: default
spec:
# Configures Calico networking.
calicoNetwork:
# Note: The ipPools section cannot be modified post-install.
ipPools:
- blockSize: 26
cidr: 10.244.0.0/16
encapsulation: VXLANCrossSubnet
natOutgoing: Enabled
nodeSelector: all()
---
# This section configures the Calico API server.
# For more information, see: https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/reference/installation/api#operator.tigera.io/v1.APIServer
apiVersion: operator.tigera.io/v1
kind: APIServer
metadata:
name: default
spec: {}
And so here it is.
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
vcp Ready control-plane 39h v1.29.2 192.168.1.70 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.1.0-18-amd64 containerd://1.7.13
vworker1 Ready <none> 39h v1.29.2 192.168.1.71 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.1.0-18-amd64 containerd://1.7.13
vworker2 Ready <none> 39h v1.29.2 192.168.1.72 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.1.0-18-amd64 containerd://1.7.13
vworker3 Ready <none> 39h v1.29.2 192.168.1.73 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.1.0-18-amd64 containerd://1.7.13
vworker4 Ready <none> 39h v1.29.2 192.168.1.74 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.1.0-18-amd64 containerd://1.7.13
vworker5 Ready <none> 39h v1.29.2 192.168.1.75 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.1.0-18-amd64 containerd://1.7.13
gitops - install and bootstrap flux¶
Here is the page I prepared apart from this lab building effort - flux
Required permissions
To bootstrap Flux, the person running the command must have cluster admin rights for the target Kubernetes cluster. It is also required that the person running the command to be the owner of the GitLab project, or to have admin rights of a GitLab group.
And here is what I actually do this time. Nothing special.
- create a new repository
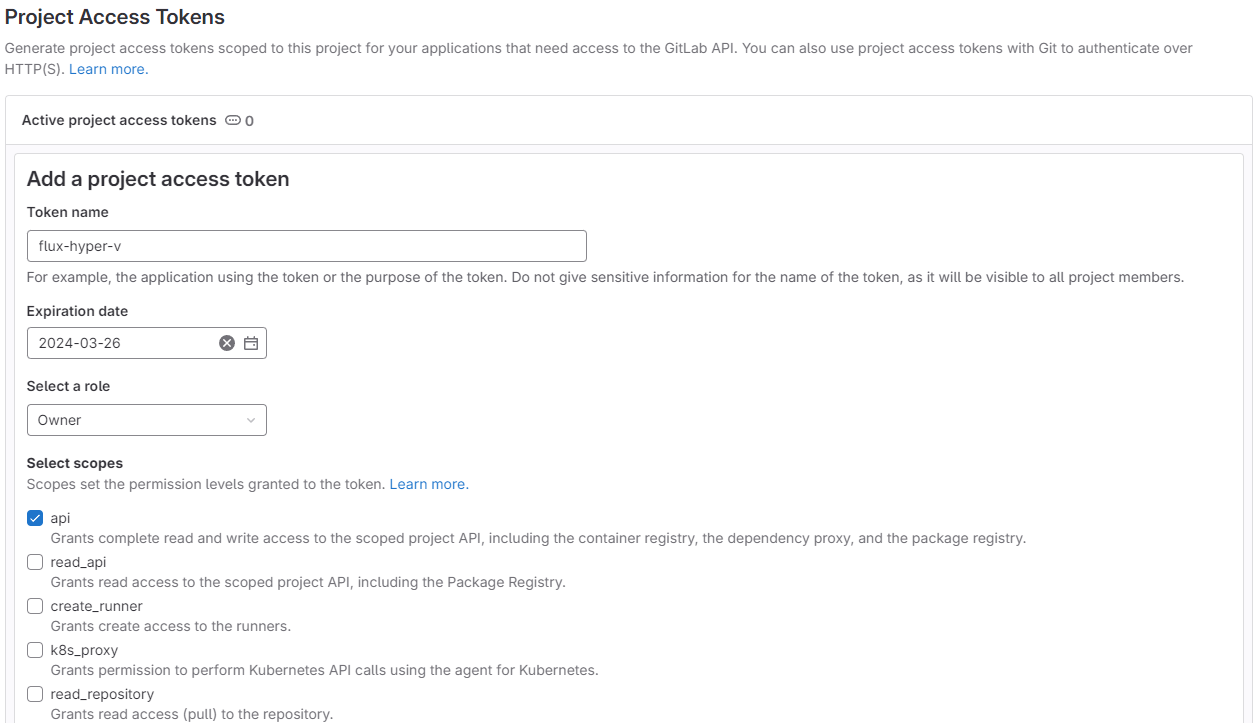
gitops/homelabon my self-managed GitLab - create an access token with owner role and api access
- install flux on whichever client machine with kubeconfig, management access to the control plane
- bootstrap
creating project access token for flux bootstrap¶
install flux¶
https://fluxcd.io/flux/installation/
https://github.com/fluxcd/flux2
bootstrap¶
export GITLAB_TOKEN={token_string_here}
export GITLAB_SERVER={gitlab_server}
flux bootstrap gitlab \
--deploy-token-auth \
--hostname="$GITLAB_SERVER" \
--owner=gitops \
--repository=homelab \
--path=./clusters/hyper-v \
--branch=main
Here is the log.
$ flux bootstrap gitlab \
--deploy-token-auth \
--hostname="$GITLAB_SERVER" \
--owner=gitops \
--repository=homelab \
--path=./clusters/hyper-v \
--branch=main
► connecting to https://cp.blink-1x52.net
► cloning branch "main" from Git repository "https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab.git"
✔ cloned repository
► generating component manifests
✔ generated component manifests
✔ committed component manifests to "main" ("0759d8f2ea8a74943868e932ebdd1d707b7c0c40")
► pushing component manifests to "https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab.git"
► installing components in "flux-system" namespace
✔ installed components
✔ reconciled components
► checking to reconcile deploy token for source secret
✔ configured deploy token "flux-system-main-flux-system-./clusters/hyper-v" for "https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab"
► determining if source secret "flux-system/flux-system" exists
► generating source secret
► applying source secret "flux-system/flux-system"
✔ reconciled source secret
► generating sync manifests
✔ generated sync manifests
✔ committed sync manifests to "main" ("3ec779843915ffad20a2dc220f5a4e65d5bdb2fa")
► pushing sync manifests to "https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab.git"
► applying sync manifests
✔ reconciled sync configuration
◎ waiting for GitRepository "flux-system/flux-system" to be reconciled
✔ GitRepository reconciled successfully
◎ waiting for Kustomization "flux-system/flux-system" to be reconciled
✔ Kustomization reconciled successfully
► confirming components are healthy
✔ helm-controller: deployment ready
✔ kustomize-controller: deployment ready
✔ notification-controller: deployment ready
✔ source-controller: deployment ready
✔ all components are healthy
$ flux get all
NAME REVISION SUSPENDED READY MESSAGE
gitrepository/flux-system main@sha1:3ec77984 False True stored artifact for revision 'main@sha1:3ec77984'
NAME REVISION SUSPENDED READY MESSAGE
kustomization/flux-system main@sha1:3ec77984 False True Applied revision: main@sha1:3ec77984
$ flux version
flux: v2.2.2
distribution: flux-v2.2.2
helm-controller: v0.37.2
kustomize-controller: v1.2.1
notification-controller: v1.2.3
source-controller: v1.2.3
sops¶
https://fluxcd.io/flux/guides/mozilla-sops/
I will make gitops/homelab-sops the repository to store encrypted secret.
First, I will generate a keypair, put it in the flux-system namespace as secret, and upload public key to the repository.
# install sops and gpg if not installed
# create gitops/homelab-sops repository on gitlab if not created yet
# set key name and comment
export KEY_NAME="hyper-v.blink-1x52.net"
export KEY_COMMENT="hyper-v flux secret"
# generate the keypair
gpg --batch --full-generate-key <<EOF
%no-protection
Key-Type: 1
Key-Length: 4096
Subkey-Type: 1
Subkey-Length: 4096
Expire-Date: 0
Name-Comment: ${KEY_COMMENT}
Name-Real: ${KEY_NAME}
EOF
# find the fingerprint of the generated keypair
# and export
gpg --list-secret-keys "${KEY_NAME}"
export KEY_FP={fingerprint of the generated keypair}
# create the secret using the keypair in the flux-system namespace
gpg --export-secret-keys --armor "${KEY_FP}" |
kubectl create secret generic sops-gpg \
--namespace=flux-system \
--from-file=sops.asc=/dev/stdin
# confirm that the secret is there
kubectl get secret -n flux-system sops-gpg
# clone and go to the homelab-sops project directory
git clone https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab-sops.git
cd homelab-sops
# create the directory for hyper-v cluster and place public key there
mkdir -p clusters/hyper-v
gpg --export --armor "${KEY_FP}" > ./clusters/hyper-v/.sops.pub.asc
# commit and push so that going forward other member or yourself on other machine can import it to encrypt and place secret manifests in this repository
# to import...
# gpg --import ./clusters/hyper-v/.sops.pub.asc
# delete the keypair from the local machine
gpg --delete-secret-keys "${KEY_FP}"
# configure encryption
cat <<EOF > ./clusters/hyper-v/.sops.yaml
creation_rules:
- path_regex: .*.yaml
encrypted_regex: ^(data|stringData)$
pgp: ${KEY_FP}
EOF
And next, I will set additional git source for flux to watch on the original gitops/homelab repository.
Unless the gitops/homelab-sops is a public repository, flux needs something to be authorized to read the repository. Let's create a token with read access for flux.
Navigate to the gitops/homelab-sops repository, settings > repository > deploy tokens, and click add token to create one. I'd name it "homelab-sops" and set "read_repository" scope to this deploy token.
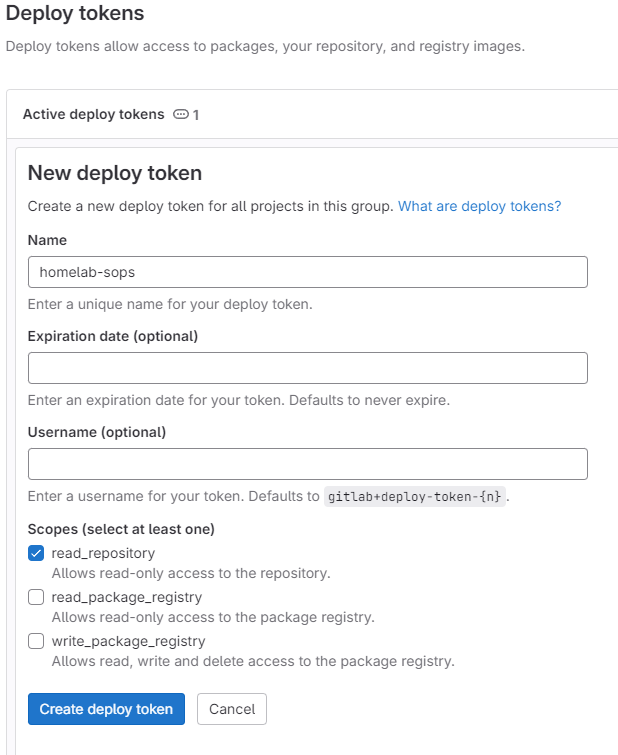
# create a secret from the deploy token to read the sops repository
flux create secret git deploy-token-homelab-sops \
--namespace=flux-system \
--username={deploy token name here} \
--password={deploy token string here} \
--url=https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab-sops.git
This probably is the last secret to manually push to the kubernetes cluster, since the gitops by flux is in place and secret encryption will be ready after sops setup.
I move on to update hyper-v cluster setup in the original gitops/homelab repository to start using the other gitops/homelab-sops repository.
# clone and go to the homelab project directory
cd ~/repos/cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops
git clone https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab.git
cd homelab
# prepare directories
mkdir -p infrastructure/controllers
mkdir -p infrastructure/configs
cd infrastructure/controllers
And in ./infrastructure/controllers directory, place this sops.yaml manifest which includes flux gitrepo, and kustomization.
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: homelab-sops
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 1m0s
ref:
branch: main
secretRef:
name: deploy-token-homelab-sops
url: https://cp.blink-1x52.net/gitops/homelab-sops.git
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: homelab-sops
namespace: flux-system
spec:
decryption:
provider: sops
secretRef:
name: sops-gpg
interval: 1m0s
path: ./clusters/hyper-v
prune: true
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: homelab-sops
I will then add ./clusters/hyper-v/infrastructure.yaml to include ./infrastructure/controllers.
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: infra-controllers
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 1m0s
path: ./infrastructure/controllers
prune: true
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system
Now everything is set. The homelab-sops flux kustomization fails until there is some manifest. I will add test secret.
# on gitops/homelab-sops repository
cd clusters/hyper-v
kubectl -n default create secret generic basic-auth \
--from-literal=user=admin \
--from-literal=password=change-me \
--dry-run=client \
-o yaml > basic-auth.yaml
sops --encrypt --in-place basic-auth.yaml
# see the secret manifest file basic-auth.yaml is now encrypted
# git commit and push
# wait for flux reconcilation
# confirm the status
flux get ks homelab-sops
# confirm the secret created
kubectl get secret basic-auth -n default -o jsonpath='{.data.user}' | base64 -d
repository structure so far¶
.
|-clusters
| |-hyper-v
| | |-infrastructure.yaml # flux kustomize to reconcile resources at ./infrastructure/controllers
| | |-flux-system # flux system installed during bootstrap
| | | |-kustomization.yaml
| | | |-gotk-sync.yaml
| | | |-gotk-components.yaml
|-infrastructure
| |-configs
| |-controllers
| | |-kustomization.yaml # k8s kustomization to include sops.yaml (and more to be added)
| | |-sops.yaml # namespace, gitrepo, and flux kustomization for sops
|-.git